Structure, Life Cycle and the Role of Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera)
Objectives
Structure and Life Cycle of Honey Bee (Apis mellifera)
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Honey bee Hive
Honey bees are social insects. There are three types of honey bees: drones, workers and queens. A colony generally contains one queen bee (a fertile female), a few thousand drone bees (fertile males) and a large population of sterile female worker bees. They construct colonial nests out of wax. The nest known as hive is made up of small hexagonal compartments called cell. The wax cells are cemented together to form a mass called honey comb.
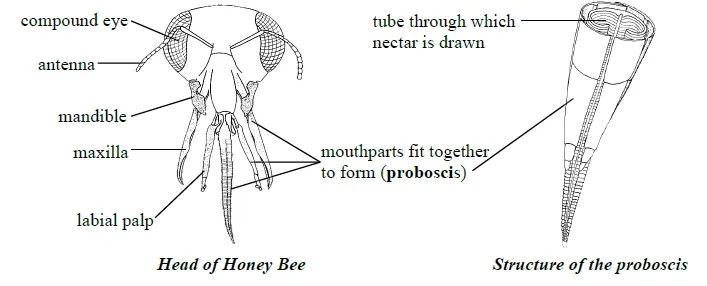
Structure of Honey Bee
The body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. The head has three simple eyes (ocelli), one pair of compound eyes and pair of antennae.
Thorax bears three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings. The fore and hind wings on each side are linked by hooks and they move together in flight.
The Workers (Sterile female Bees)
The workers are sterile female bees. They are the smallest and numerous members.
The head bears mouth parts made up of proboscis and mandibles. The proboscis is used in sucking up nectar and mandibles for chewing pollen, constructing wax and cell.
There are three pairs of specialized legs.
1. The fore leg bears small depression lined with hairs forming a comb. The comb is used to clean pollen off its head, antennae and proboscis.2. The middle leg has strong hair-like structure called prong on tibia, used for digging out the pollen from the pollen basket and for picking wax.
Worker has a series of glands on the abdomens which secrete wax. Workers use the wax to build hive and repair it with propolis (a glue substance from certain plants).
Function of Worker Bees
2. collection of pollen, nectar and propolis
3. make the wax cells
4. clean and repair hive
5. guard and protect the hive
6. ventilating the hive on hot days
7. foraging
The Queen (Fertile Female Bees)
The queen is a fertile female. It is created as the workers feed a larva with only royal jelly throughout its development, rather than pollen grains.
The mouthparts are poorly developed. The legs are not specialized as in workers.
It has a relatively longer abdomen and a shorter wings than other members of the colony. The sting of queens is not barbed like a worker's sting.
Function: is solely egg-laying
The Drones (Fertile Male Bees)
The drones are fertile males. They have poorly developed mouthparts. Drones do not have a sting and pollen basket.
The drones do not work inside the hive. They are fed by the workers or help themselves from the store of pollen and nectar in the combs.
Function: is to mate with a new queen.
Mode of Life of Honey Bees
Feeding in Honey Bees
Honey bee feed entirely on pollen and nectar. Pollen is mainly protein, and nectar is mainly carbohydrate.
The nectar is sucked from the flowers by means of a proboscis. Bees collect pollen in the pollen basket and carry it back to the hive.
When a bee visits a flower, its body becomes dusted with pollen. The hind legs are adapted to comb the pollen off the body, compact it and store it as ‘pollen sacs’.
Honey is made when the nectar and sweet deposits from plants are gathered, modified and stored in the honeycomb as a food source for the colony.
How Honey Bees Communicate and Behave
When a worker bee finds source of nectar, it returns to the hive and communicate to others by using a pattern of dancing known as the bee dance or waggle dance.
A worker bee performs the dance on the vertical comb. The angle between the central line and the vertical represents the angle between the source, the hive and the sun. The degree of ‘waggle’ in this line indicates the distance; more waggle means greater distance.
If the source is very close to the hive, it may also exhibit a less specific dance commonly known as the "Round Dance". Honey bees also perform tremble dances, which recruit receiver bees to collect nectar from returning foragers.
Life Cycle of Honey Bees
A new queen goes on nuptial flights and mate with one drone. The drone dies in the act of mating, as his reproductive organs ripped out of his body during mating.
The queen mates only once in her life and once mated, it may lay up to 2000 eggs per day.
It lay eggs and fertilizes them with the sperms stored in the spermatheca. Eggs are laid singly in a cell. The workers build three types of wax cell, differing in size or shape.
Using her spermatheca, the queen can choose to fertilize the egg she is laying, usually depending on the cell she is laying in.
Drones are developed from unfertilized eggs while females (queens and worker bees) develop from fertilized eggs.
After hatching, only the queen larvae are fed with regurgitating protein-rich, milky secretion called royal jelly, which comes from the salivary glands of workers.
The difference in diet causes the workers to be sterile and the queen to be fertile.
The workers feed the larvae until they are ready to pupate and then they put a wax capping over the cell. After 10-11 days the capping is bitten off and the young adult emerges.
Economic Importance of Honey Bees
Honey bees are more than just producers of honey; they are integral to various economic activities and industries. Their contributions extend beyond their role in pollination, impacting agriculture, manufacturing, and even health sectors. Here’s a detailed look at the economic importance of honey bees:
1. Bees' Role in Pollination
Honey bees are crucial pollinators for many crops and wild plants. They facilitate the fertilization of flowers by transferring pollen, which enables plants to produce seeds and fruits. This process is essential for the production of a vast array of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. The value of pollination services provided by honey bees is immense, with estimates suggesting that they contribute billions of dollars to global agriculture. For example, crops such as almonds, apples, and blueberries depend heavily on honey bee pollination to achieve optimal yields and quality .
2. Beeswax Production
Beeswax, a natural substance produced by honey bees, has various applications in different industries. It is used in the production of products such as polishes, candles, and body creams. Beeswax’s natural properties make it ideal for creating non-toxic and hypoallergenic products, which are highly valued in consumer markets. Additionally, beeswax is used in the formulation of some pharmaceuticals and cosmetics due to its emollient and moisturizing characteristics .
3. Honey as a Food Source
Honey, produced by honey bees from nectar, is a valuable food source with both nutritional and economic significance. It is used as a natural sweetener and has been a staple in human diets for centuries. Beyond its role in cooking and baking, honey also has medicinal properties and is used in traditional remedies. The production and sale of honey contribute significantly to the income of beekeepers and support local economies .
4. Honey in Sweet Products
Honey is a key ingredient in various sweet products, including toffees, biscuits, and certain syrups. Its natural sweetness and unique flavor make it a preferred choice for many food manufacturers. Additionally, honey is used in the production of some drugs and medicinal syrups due to its therapeutic properties. This wide range of applications highlights the versatility of honey and its importance in the food industry .
5. Economic Impact of Bee Stings
While bee stings can cause pain and, in rare cases, severe allergic reactions or death, they also have an economic impact. The medical costs associated with treating severe allergic reactions to bee stings can be significant. However, this is often outweighed by the economic benefits derived from honey bee products and services. Additionally, the honey bee industry supports many jobs and contributes to the overall economic health of agricultural communities .
6. Propolis and Its Uses
Propolis, a resin-like substance produced by bees, has various uses in both health and cosmetic industries. It is consumed by humans as a health supplement due to its potential antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Propolis is also used in some cosmetic products for its skin-healing and anti-aging benefits. The demand for propolis in health supplements and cosmetics adds another economic dimension to the beekeeping industry .
7. Additional Economic Contributions
Beyond the points mentioned, honey bees also contribute to the economic landscape through educational and recreational activities. Beekeeping as a hobby or profession supports local economies through farmers’ markets, agricultural fairs, and educational programs on pollination and sustainable practices. The increased awareness of the importance of bees also drives funding and research into bee conservation, further supporting economic growth in related sectors .
For more detailed information on the economic impact of honey bees and their products, explore these resources:
The Role of Honey Bees in Pollination
Honey bees play an indispensable role in the pollination of many plants, which is essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Their activities significantly impact both natural ecosystems and agricultural systems, highlighting their importance beyond honey production.
1. Mechanics of Pollination
Honey bees are remarkable pollinators due to their behavior and physical adaptations. When bees visit flowers to collect nectar and pollen, they inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another. This process fertilizes the plants, enabling them to produce seeds and fruit. Honey bees have specialized body structures, such as branched hairs and a pollen basket on their hind legs, which facilitate efficient pollen collection and transfer.
2. Impact on Agriculture
Honey bees are crucial for the pollination of many crops. Approximately 70 of the top 100 crops that feed the world rely on animal pollination, with honey bees being the primary pollinators for many of these . Crops like almonds, apples, blueberries, and cucumbers depend heavily on honey bee activity for optimal yields. The economic value of honey bee pollination services is estimated to be billions of dollars annually, underscoring their importance to global food security.
3. Enhancing Crop Yields and Quality
Studies have shown that honey bee pollination can lead to increased crop yields and improved fruit quality. For instance, pollinated apples and strawberries tend to be larger and more uniformly shaped compared to those that have not been pollinated by bees . This increase in crop yield and quality is vital for farmers, as it directly affects their profitability and the availability of fresh produce.
4. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Beyond agriculture, honey bees contribute to the health and diversity of natural ecosystems. By pollinating wild plants, they support the growth of native flora that provides habitat and food for various wildlife species. This process helps maintain ecological balance and promotes biodiversity. The decline of honey bee populations can disrupt these natural systems, leading to decreased plant diversity and the loss of habitat for other species .
5. Challenges and Conservation
Honey bee populations are facing significant challenges, including habitat loss, pesticide exposure, disease, and climate change. These threats have led to declines in bee populations worldwide, raising concerns about their ability to perform their essential pollination role. Conservation efforts are crucial to address these issues, including creating bee-friendly habitats, reducing pesticide use, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices .
For further reading and detailed information on the role of honey bees in pollination, check out the following resources:
- FAO: Importance of Honey Bees
- American Bee Journal: Impact on Crop Yields
- EPA: Honey Bees and Ecosystem Health
- Bee Informed Partnership: Challenges and Conservation
The Role of Bees in Ecosystems
Bees are vital to the health and sustainability of ecosystems around the world. Their role extends beyond producing honey, as they are key pollinators for many plants, including those crucial for human food production. Understanding the importance of bees helps us appreciate their contribution to biodiversity and the natural balance of our environment.
1. Pollination and Plant Diversity
Bees are essential pollinators for a wide variety of plants, including many that humans rely on for food. Approximately 75% of the world's flowering plants and 35% of global food crops depend on animal pollinators, with bees being the most efficient . By transferring pollen from one flower to another, bees enable plants to produce fruits and seeds, which are critical for plant reproduction and genetic diversity. This process not only supports the plants themselves but also the animals and insects that feed on them, maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
2. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability
The presence of bees in an ecosystem contributes significantly to biodiversity. A diverse plant community supports a variety of wildlife, including birds, mammals, and other insects, creating a stable and resilient ecosystem. Bees pollinate many wild plants, ensuring the survival of species that may not be directly useful to humans but are crucial for ecological balance. The decline in bee populations, often due to habitat loss, pesticides, and diseases, can lead to a reduction in plant diversity and a subsequent decrease in the species that depend on these plants .
3. Support for Food Chains
Bees play a foundational role in food chains by supporting plants that provide food and habitat for other organisms. Many animals, such as birds and small mammals, rely on the seeds, fruits, and plants pollinated by bees for sustenance. This interdependence highlights the critical nature of bees in maintaining the flow of energy through ecosystems .
4. Economic and Environmental Impact
The economic value of bees extends beyond honey production. The pollination services they provide are estimated to be worth billions of dollars annually to agriculture. Crops such as apples, almonds, and berries, which require or benefit from bee pollination, are crucial for both food security and economic stability . Moreover, the environmental benefits of healthy bee populations include promoting plant growth, reducing soil erosion, and improving water quality through the maintenance of diverse plant communities.
5. Conservation Efforts and the Future
The decline in bee populations has raised global concern, leading to increased efforts to protect and conserve these vital insects. Conservation strategies include creating bee-friendly habitats, reducing pesticide use, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices. By understanding and addressing the challenges bees face, we can ensure their survival and the continued health of our ecosystems .
For more detailed information and resources on the role of bees in ecosystems, you can visit the following links:
References
- "Importance of Pollinators in Agriculture" - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- "Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services" - Convention on Biological Diversity
- "The Role of Pollinators in Food Production" - United Nations Environment Programme
- "Economic Value of Bee Pollination" - National Agricultural Statistics Service
- "Conservation Strategies for Bees" - International Union for Conservation of Nature
- "Economic Value of Pollination Services" - Pollinator Partnership
- "Beeswax Production and Uses" - Beeswax Co.
- "The Importance of Honey in Human Diets" - National Honey Board
- "Honey and Sweet Product Manufacturing" - Food and Agriculture Organization
- "Health Impacts of Bee Stings" - American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology
- "Propolis: Uses and Benefits" - Propolis Research Society
Free Notes on Structure and Mode Life Cycle of Honey Bee
Download Free PDF on: Structure and Life Processes of Honey Bee