Exploring Butterfly Anatomy and Life Processes: A Comprehensive Guide
Objectives
Structure and the Life Processes of Butterfly
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Butterflies are complex insects with specialized structures and life processes that enable them to survive, grow, and reproduce. Understanding these structures and processes provides insight into the fascinating biology of butterflies.
Most species are diurnal (mainly day-flying insect). Butterflies feed on nectar of flower.
Structure of Butterfly
The body is divided into three segments: the head, thorax, and the abdomen.
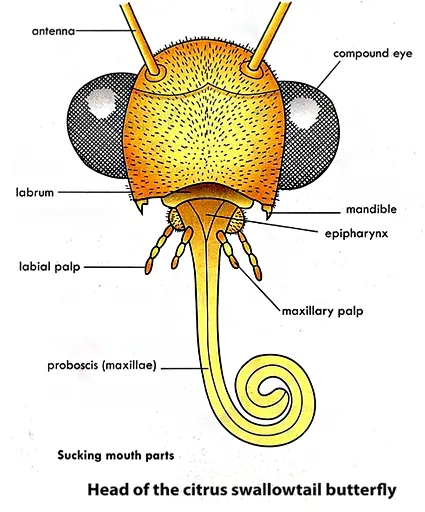
The head bears a pair of compound eyes, a mouthparts and a pair of prominent antennae with knob at the tip.
The mouthparts is modified into long tube called proboscis, which is used for sucking nectar. The proboscis is formed from a pair of maxillae. It is coiled up when not in used. The head is covered by hair-like scales.
The thorax consists of three segments; prothorax, metathorax and mesothorax, each bearing a pair of jointed walking legs. The thorax is hairy.
The mesothorax and metathorax bear a pair of membranous wings each. The wings are clothed with scales often of bright colors. Scales also cover the head, parts of the thorax and abdomen as well as parts of the genitalia.
The abdomen is composed of ten segments. The anus is situated on the last segment.
For a detailed look at butterfly anatomy, visit the Smithsonian Institution's page on butterflies
Life Processes of Butterfly
Nutrition
- Larvae: Caterpillars consume large amounts of plant material, providing the energy needed for growth and development.
- Adults: Butterflies primarily feed on nectar from flowers. Some species also feed on fruit, tree sap, and other organic materials.
For a comprehensive guide on butterfly diets, visit Butterfly Conservation's feeding page.
Sensory Perception
- Vision: Butterflies have excellent color vision and can see ultraviolet light, which helps them locate flowers.
- Smell: Antennae are crucial for detecting chemical cues in the environment, such as pheromones and floral scents.
Life Cycle of Butterfly
The life cycle of butterfly shows complete metamorphosis: egg; larva or caterpillar; pupa or chrysalis; and imago or adult.
Eggs
Butterfly is oviparous or egg-layers. After mating eggs are laid either singly or in small groups on the undersurface of food plants; cabbages and young citrus leaves.
The egg is spherical, whitish, pale green in color and with almost smooth outer shell. The eggs hatch in few weeks, into larvae called caterpillar.
For more detailed information about butterfly eggs, check out this National Wildlife Federation article.
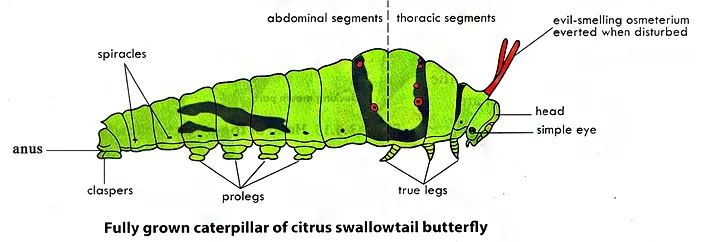
Caterpillar
It has three distinct body parts: the head, the thorax and the abdomen. The head has a pair of short antennae, mouthparts, and six pairs of simple eyes called ocelli.
Each of the three thoracic segment bears a pair of jointed true legs which ends with claw.
The abdomen is composed of ten segments. The 3rd to 6th abdominal segments bear a pair of false legs called prolegs. The prolegs have tiny hooks known as crochets that hold the larva onto its silk mat or leaf. Clasper is borne on the last segment.
Some caterpillars have the ability to inflate parts of their head to appear snake-like. They have false eye-spots to enhance this effect. Some caterpillars have special structures called osmeteria (singular: osmeterium) which emit foul smelling chemicals. These are used in defense.
Caterpillars are ‘eating machines’. They actively feed plant leaves and spend practically their time in search of food. Caterpillars undergo ecdysis and develop through four stages or instars before changing into pupa or chrysalis.
Learn more about caterpillars and their behaviors on the Butterfly Conservation website
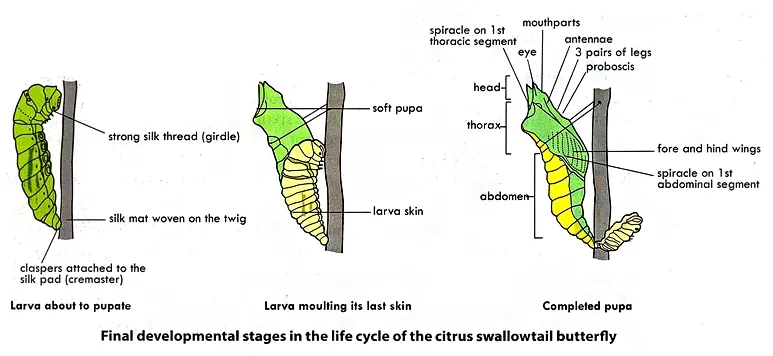
Pupa/Chrysalis
The pupa is a resting stage where all the tissues in the caterpillar's body are rearranged.
The caterpillar stops feeding and attach itself to a stem or leaf. It secretes a silk pad called a cremaster on the twig and attaches its claspers to it.
It is held in upright position by secreting silk girdle around the thorax.
The chrysalis usually moves the abdominal segments rapidly or produce sounds to scare potential predators.
The internal structures of the caterpillar break down and re-organized into adult organs. The chrysalis becomes almost transparent when the butterfly is about to emerge.
The pupal stage lasts for about 11 days.
For a deeper dive into the chrysalis stage, visit this article by the University of Florida.
Adult/Imago
The adult, sexually mature stage of the insect is known as the imago. When an adult emerges from the split chrysalis, it hangs upside down and pumps blood into its delicate wings and waits for them to dry. It can fly a few hours after emerging.
Explore more about adult butterflies and their behaviors at the North American Butterfly Association.
Difference between Butterfly and Moth
Butterfly | Moth |
It is a diurnal insect | It is a nocturnal insect |
It has antenna with knob at the tip | The tip of the antenna is pointed |
It has brightly scales on its body | It is dull colored |
The wings are separated and not joined | The wings are connected to each other |
When at rest the wings are folded vertically | The wings are spread horizontally at rest |
Economic Importance of butterfly
Butterflies, beyond their aesthetic appeal, play significant roles in various economic sectors, particularly in agriculture, tourism, and research. Here's a detailed exploration of their economic importance:
For further information on the economic importance of butterflies, reputable sources include Butterfly Conservation, the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation, and scientific journals on entomology and conservation.
Control of Caterpillar of Butterfly
Caterpillars, the larval stage of butterflies, can sometimes cause significant damage to plants as they feed voraciously. While butterflies are beneficial pollinators, controlling caterpillar populations is important in gardens and agricultural settings to protect crops and ornamental plants. Here are some effective methods for managing caterpillar populations.
1. Biological Control
- Predatory Insects: Introducing natural predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps can help keep caterpillar populations in check. These insects prey on caterpillars, reducing their numbers naturally.
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): This naturally occurring bacterium is effective against many caterpillar species. When caterpillars ingest Bt, it produces toxins that target their digestive systems, leading to death. Bt is safe for humans, pets, and beneficial insects.
For more information on biological control, visit the University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources.
2. Physical Control
- Handpicking: For smaller infestations, handpicking caterpillars off plants can be an effective method. Wear gloves and drop the caterpillars into a bucket of soapy water to dispose of them.
- Barriers: Installing physical barriers such as fine mesh or row covers can prevent adult butterflies from laying eggs on plants. This is particularly useful in vegetable gardens.
Explore more about physical control methods on the Royal Horticultural Society website.
3. Chemical Control
- Insecticidal Soaps: These are a safer option for controlling caterpillars, especially in organic gardens. They work by breaking down the outer protective layer of caterpillars, causing them to dehydrate and die.
- Synthetic Insecticides: In severe cases, synthetic insecticides may be necessary. Products containing ingredients like spinosad or pyrethroids can be effective. However, these should be used as a last resort due to their potential impact on beneficial insects and the environment.
For guidelines on using chemical control safely, check out the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) resources.
4. Cultural Control
- Crop Rotation: Changing the types of plants grown in a particular area each season can disrupt the life cycle of caterpillars, reducing their numbers.
- Sanitation: Removing plant debris and fallen leaves from the garden helps eliminate potential breeding grounds for caterpillars.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Combining various control methods into an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach can provide the most effective and sustainable solution for managing caterpillar populations. IPM emphasizes using the least harmful methods first and integrating biological, physical, chemical, and cultural controls as needed.
Conclusion
The structure and life processes of butterflies are intricately designed to support their survival and reproduction. From their specialized external structures to their complex life cycle and sensory abilities, butterflies are remarkable examples of adaptation and evolution. Understanding these aspects not only enriches our appreciation of butterflies but also highlights the importance of conserving their natural habitats.
For further reading on butterfly biology and conservation, visit the World Wildlife Fund's butterfly section.
Get Your Free PDF!
Download our comprehensive guide to Structure and the Life Processes of Butterfly to boost your knowledge.
Download PDFClick the button above to get instant access to the PDF.


.webp)